
The States Losing the Most Land to Wildfires, Mapped
Forest fires get worse in the United States thanks Climateand Wrong forest managementAnd increase building And development in the areas exposed to the fire,
Although the number of fires per year has not increased since the 1980s, the total area of the burning lands for sure, according to The National Center for Fire Fire between the agencies, from 2 to 3 million acres annually to about 7 million acres for a year in the past decade. 10 million burned acres recorded in 2020.
Forest fires are not evenly distributed throughout the country, although some states are more likely to be more likely than others.
The threat of the wildfire increases in general
Unfortunately, it is a global trend. In 2023 and 2024, more than 78 million acres of forests were burned all over the world, which is twice the average period of the past two years of the past two decades, according to a speech. Ticket In the magazine The facts of the National Academy of Sciences.
The risk of wild fires is not distributed evenly throughout the United States, as shown in maps From the non -partisan data collection site Usafacts.org.
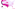
In 2023, it was the first five countries that lost the largest number of spaces focused in the west and southwest:
- California: 332,722 acres
- Alaska: 314,276 acres
- New Mexico: 212,378 acres
- Texas: 210,264 acres
- Oregon: 202,035 acres
The countries with the least lost fires in fires were relatively small and cold. She was:
- Dilayer: 0 acres
- New Hampshire: 58 acres
- Vermont: 62 acres
- Kentucky: 70 acres
- Connecticut: 297 acres
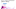
When considering the number of burning acres per 10,000 acres of land, the map appears slightly different. Countries were the highest concentrations of forest fires:
- Nebraska: 36.5 acres of wildfire per 10,000 acres
- Oklahoma: 36.3 acres of wildfire per 10,000 acres
- Washington: 33.2 acres of wildfire per 10,000 acres
- New Jersey: 32.3 acres of washing per 10,000 acres
- Oregon State: 32.1 acres of wildfire per 10,000 acres
More forest fires is part of a long -term direction
None of this should be surprising. California – which witnessed some of the most destructive forest fires and the two fatwas in its history Earlier this yearIt features a mixture of dry air, dry plants, strong winds and high population density (causing humans About 85 percent Of the forest fires (which makes the state a Tinder Fund. Some of these factors also affect New Mexico, Texas and Oregon.
Alaska is different. Drought and lightning courses make forest fires part of their natural ecosystem, but this course Abnormal. According to the statements of the US Department of Agriculture, an area of 2.5 times has been burned between 2000 and 2020 compared to the previous two subsidies, and three years of the four years have been burned since 2000.
The situation is expected to get worse, as climate change continues to increase temperatures and lead to greater evaporation, leaving dry and ready -made conditions. The annual season is expected to be the biggest risk in the future. Scientists from the Arjun National Laboratory and the University of Wisconsin Madison have Propagate By the end of the century, the threat of a 10 -day wildfire will increase by average across the continental United States, and some regions, such as the Great Southern Plains, will be more than 40 additional days of severe risks.
Discover more stories about the environment:













Post Comment